Editor(s): Zhi-gang Zheng, Wei Hu, Chen-hui Peng
Year: 2020
Status: Published
Compared with solid materials, soft matters have inherent advantages such as excellent adjustability, high flexibility, scalable size, ease of manufacture, and environmental adaptation. The various interesting properties of soft matter are not only worthy of basic research, but also inspires fantastic applications, especially in photonics. Therefore, this topic focuses on researches about liquid crystal and soft matter photonics. This special issue aims to attract research on soft matter photonics (Soft Mattonics) and promote the development of related applications.
Soft-matter photonics (soft mattonics) is an emerging and active area that has attracted widespread attention in recent years. Compared with solid materials, soft matters exhibit inherent advantages such as excellent adjustability, high flexibility, scalable size, ease of manufacture, and environmental adaptation. This special issue focuses on various interesting optical properties and fantastic photonic applications of soft matters including different liquid crystal (LC) phases, stimuli-responsive polymers, and even silks. This special issue aims to present the impressive progresses on soft mattonics and promote developments of related applications.
Diffractive optical elements attract a considerable amount of attention, mainly due to their potential applications in imaging coding, optical sensing, etc. Application of ferroelectric liquid crystals (FLCs) with photo-alignment technology in diffractive optical elements results in a high efficiency and a fast response time. In this study we demonstrate a circular Dammann grating (CDG) with a diffraction efficiency of 84.5%. The achieved response time of 64 μs is approximately two orders of magnitude faster than the existing response time of nematic liquid crystal devices. By applying a low electric field (V = 6 V) to the FLC CDG, it is switched between the eight-order diffractive state and the transmissive diffraction-free state.
In this Letter, we propose that the photopatterned liquid crystal (LC) can act as a broadband and efficient terahertz (THz) Bessel vortex beam (BVB) generator. The mechanism lies in the frequency-independent geometric phase modulation induced by the spatially variant LC directors. By adopting large birefringence LCs and optimizing the cell gap, the maximized mode conversion efficiency can be continuously adjusted in broadband. Furthermore, the LC patterns can be designed and fabricated at will, which enables the THz BVBs to carry various topological charges. Such a THz LC BVB generator may facilitate the advanced THz imaging and communication apparatus.
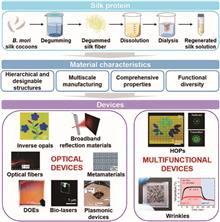
The growing demand of sustainable and biocompatible optical devices is stimulating the development of naturally derived biomaterials for optics and photonics. As a versatile biomaterial, silk provides excellent material characteristics that are favorable towards the generation of advanced optical systems. This review examines the use of silk as a material platform in optical applications. Recent advances in silk-based optical devices and multifunctional devices are summarized. The challenges and directions in further designing and fabricating silk optics are also discussed. We envision that silk will play a pivotal role in the future exploitation of sustainable, intelligent, wearable/implantable, and multifunctional optical devices.
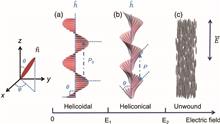
The dynamic manipulation of the helicity in a cholesteric helical superstructure could enable precise control over its physical and chemical properties, thus opening numerous possibilities for exploring multifunctional devices. When cholesteric material satisfies the sufficiently small bending elastic effect, an electrically induced deformation named the cholesteric heliconical superstructure is formed. Through theoretical and numerical analysis, we systematically studied the tunable helicity of the heliconical superstructure, including the evolution of the corresponding oblique angle and pitch length. To further confirm the optical properties, Berreman’s 4 × 4 matrix method was employed to numerically analyze the corresponding structure reflection under the dual stimuli of chirality and electric field.
The method for batch continuous production of polymerized cholesteric liquid crystal (PCLC) microdisks based on centrifugal microfluidics was proposed. The prototype centrifugal microfluidic chip was fabricated by the wet-etching technique with a series of ladder-like concentric ring channels whose depths decrease radially. Two types of dye-doped PCLC microdisks with different doping procedures were generated by this method, the tunable lasing properties were characterized, and corresponding potential applications in a micro-cavity laser and optical barcode were demonstrated. The method is also applicable to a broad range of other polymerized materials.
We report holographic fabrication of nanoporous distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) films with periodic nanoscale porosity via a single-prism conuration. The nanoporous DBR films result from the phase separation in a material recipe, which consists of a polymerizable acrylate monomer and nonreactive volatile solvent. By changing the interfering angle of two laser beams, we achieve the nanoporous DBR films with highly reflective red, green, and blue colors. The reflection band of the nanoporous DBR films can be tuned by further filling different liquids into the pores inside the films, resulting in the color change accordingly. Experimental results show that such kinds of nanoporous DBR films could be potentially useful for many applications, such as color filters and refractive index sensors.
The generation of an autofocusing circular Airy beam (CAB) is realized via a liquid crystal (LC) geometric phase plate with a simple configuration. The fabrication of the LC plate is based on the photoalignment technology and dynamic exposure skill. A focal length of 74 cm is obtained, and the propagation dynamics are consistent with the simulations. Besides, a defocusing CAB is also generated, and the switch between the autofocusing and defocusing CABs can be achieved by controlling the input polarization state. This work provides a convenient and flexible approach to acquire CABs, which will promote the CAB-related applications and researches.