View fulltext
View fulltext
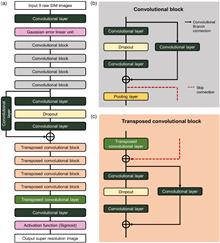
Structure illumination microscopy (SIM) imposes no special requirements on the fluorescent dyes used for sample labeling, yielding resolution exceeding twice the optical diffraction limit with low phototoxicity, which is therefore very favorable for dynamic observation of live samples. However, the traditional SIM algorithm is prone to artifacts due to the high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) requirement, and existing deep-learning SIM algorithms still have the potential to improve imaging speed. Here, we introduce a deep-learning-based video-level and high-fidelity super-resolution SIM reconstruction method, termed video-level deep-learning SIM (VDL-SIM), which has an imaging speed of up to 47 frame/s, providing a favorable observing experience for users. In addition, VDL-SIM can robustly reconstruct sample details under a low-light dose, which greatly reduces the damage to the sample during imaging. Compared with existing SIM algorithms, VDL-SIM has faster imaging speed than existing deep-learning algorithms, and higher imaging fidelity at low SNR, which is more obvious for traditional algorithms. These characteristics enable VDL-SIM to be a useful video-level super-resolution imaging alternative to conventional methods in challenging imaging conditions.
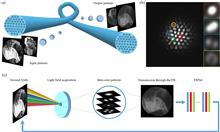
Optical fiber bundles frequently serve as crucial components in flexible miniature endoscopes, transmitting end-to-end images directly for medical and industrial applications. Each core usually acts as a single pixel, and the resolution of the image is limited by the core size and core spacing. We propose a method that exploits the hidden information embedded in the pattern within each core to break the limitation and obtain high-dimensional light field information and more features of the original image including edges, texture, and color. Intra-core patterns are mainly related to the spatial angle of captured light rays and the shape of the core. A convolutional neural network is used to accelerate the extraction of in-core features containing the light field information of the whole scene, achieve the transformation of in-core features to real details, and enhance invisible texture features and image colorization of fiber bundle images.