View fulltext
View fulltext
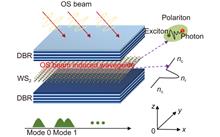
The recent era of fast optical manipulation and optical devices owe a lot to exciton-polaritons being lighter in mass, faster in speed and stronger in nonlinearity due to hybrid light-matter characteristics. The room temperature existence of polaritons in two dimensional materials opens up new avenues to the design and analysis of all optical devices and has gained the researchers attention. Here, spin-selective optical Stark effect is introduced to form a waveguide effect in uniform community of polaritons, and is used to realize polarization modulation of polaritons. The proposed device basically takes advantage of the spin-sensitive properties of optical Stark effect of polaritons inside the WS2 microcavity so as to guide different modes and modulate polarization of polaritons. It is shown that polaritonic wavepacket of different mode profiles can be generated by changing intensity of the optical Stark beam and the polarization of polaritons can be controlled and changed periodically along the formed waveguide by introduction birefringence that is sensitive to polarization degree of the optical Stark beam.The recent era of fast optical manipulation and optical devices owe a lot to exciton-polaritons being lighter in mass, faster in speed and stronger in nonlinearity due to hybrid light-matter characteristics. The room temperature existence of polaritons in two dimensional materials opens up new avenues to the design and analysis of all optical devices and has gained the researchers attention. Here, spin-selective optical Stark effect is introduced to form a waveguide effect in uniform community of polaritons, and is used to realize polarization modulation of polaritons. The proposed device basically takes advantage of the spin-sensitive properties of optical Stark effect of polaritons inside the WS2 microcavity so as to guide different modes and modulate polarization of polaritons. It is shown that polaritonic wavepacket of different mode profiles can be generated by changing intensity of the optical Stark beam and the polarization of polaritons can be controlled and changed periodically along the formed waveguide by introduction birefringence that is sensitive to polarization degree of the optical Stark beam.
On-chip manipulation of the spatiotemporal characteristics of optical signals is important in the transmission and processing of information. However, the simultaneous modulation of on-chip optical pulses, both spatially at the nano-scale and temporally over ultra-fast intervals, is challenging. Here, we propose a spatiotemporal Fourier transform method for on-chip control of the propagation of femtosecond optical pulses and verify this method employing surface plasmon polariton (SPP) pulses on metal surface. An analytical model is built for the method and proved by numerical simulations. By varying space- and frequency-dependent parameters, we demonstrate that the traditional SPP focal spot may be bent into a ring shape, and that the direction of propagation of a curved SPP-Airy beam may be reversed at certain moments to create an S-shaped path. Compared with conventional spatial modulation of SPPs, this method offers potentially a variety of extraordinary effects in SPP modulation especially associated with the temporal domain, thereby providing a new platform for on-chip spatiotemporal manipulation of optical pulses with applications including ultrafast on-chip photonic information processing, ultrafast pulse/beam shaping, and optical computing.On-chip manipulation of the spatiotemporal characteristics of optical signals is important in the transmission and processing of information. However, the simultaneous modulation of on-chip optical pulses, both spatially at the nano-scale and temporally over ultra-fast intervals, is challenging. Here, we propose a spatiotemporal Fourier transform method for on-chip control of the propagation of femtosecond optical pulses and verify this method employing surface plasmon polariton (SPP) pulses on metal surface. An analytical model is built for the method and proved by numerical simulations. By varying space- and frequency-dependent parameters, we demonstrate that the traditional SPP focal spot may be bent into a ring shape, and that the direction of propagation of a curved SPP-Airy beam may be reversed at certain moments to create an S-shaped path. Compared with conventional spatial modulation of SPPs, this method offers potentially a variety of extraordinary effects in SPP modulation especially associated with the temporal domain, thereby providing a new platform for on-chip spatiotemporal manipulation of optical pulses with applications including ultrafast on-chip photonic information processing, ultrafast pulse/beam shaping, and optical computing.
Electrochemical oxidation/reduction of radicals is a green and environmentally friendly approach to generating fuels. These reactions, however, suffer from sluggish kinetics due to a low local concentration of radicals around the electrocatalyst. A large applied electrode potential can enhance the fuel generation efficiency via enhancing the radical concentration around the electrocatalyst sites, but this comes at the cost of electricity. Here, we report about a ~45% saving in energy to achieve an electrochemical hydrogen generation rate of 3×1016molecules cm–2s–1 (current density: 10 mA/cm2) through localized electric field-induced enhancement in the reagent concentration (LEFIRC) at laser-induced periodic surface structured (LIPSS) electrodes. The finite element model is used to simulate the spatial distribution of the electric field to understand the effects of LIPSS geometric parameters in field localization. When the LIPSS patterned electrodes are used as substrates to support Pt/C and RuO2electrocatalysts, the η10 overpotentials for HER and OER are decreased by 40.4 and 25%, respectively. Moreover, the capability of the LIPSS-patterned electrodes to operate at significantly reduced energy is also demonstrated in a range of electrolytes, including alkaline, acidic, neutral, and seawater. Importantly, when two LIPSS patterned electrodes were assembled as the anode and cathode into a cell, it requires 330 mVs of lower electric potential with enhanced stability over a similar cell made of pristine electrodes to drive a current density of 10 mA/cm2. This work demonstrates a physical and versatile approach of electrode surface patterning to boost electrocatalytic fuel generation performance and can be applied to any metal and semiconductor catalysts for a range of electrochemical reactions.Electrochemical oxidation/reduction of radicals is a green and environmentally friendly approach to generating fuels. These reactions, however, suffer from sluggish kinetics due to a low local concentration of radicals around the electrocatalyst. A large applied electrode potential can enhance the fuel generation efficiency via enhancing the radical concentration around the electrocatalyst sites, but this comes at the cost of electricity. Here, we report about a ~45% saving in energy to achieve an electrochemical hydrogen generation rate of 3×1016molecules cm–2s–1 (current density: 10 mA/cm2) through localized electric field-induced enhancement in the reagent concentration (LEFIRC) at laser-induced periodic surface structured (LIPSS) electrodes. The finite element model is used to simulate the spatial distribution of the electric field to understand the effects of LIPSS geometric parameters in field localization. When the LIPSS patterned electrodes are used as substrates to support Pt/C and RuO2electrocatalysts, the η10 overpotentials for HER and OER are decreased by 40.4 and 25%, respectively. Moreover, the capability of the LIPSS-patterned electrodes to operate at significantly reduced energy is also demonstrated in a range of electrolytes, including alkaline, acidic, neutral, and seawater. Importantly, when two LIPSS patterned electrodes were assembled as the anode and cathode into a cell, it requires 330 mVs of lower electric potential with enhanced stability over a similar cell made of pristine electrodes to drive a current density of 10 mA/cm2. This work demonstrates a physical and versatile approach of electrode surface patterning to boost electrocatalytic fuel generation performance and can be applied to any metal and semiconductor catalysts for a range of electrochemical reactions.
The Microchip Imaging Cytometer (MIC) is a class of integrated point-of-care detection systems based on the combination of optical microscopy and flow cytometry. MIC devices have the attributes of portability, cost-effectiveness, and adaptability while providing quantitative measurements to meet the needs of laboratory testing in a variety of healthcare settings. Based on the use of microfluidic chips, MIC requires less sample and can complete sample preparation automatically. Therefore, they can provide quantitative testing results simply using a finger prick specimen. The decreased reagent consumption and reduced form factor also help improve the accessibility and affordability of healthcare services in remote and resource-limited settings. In this article, we review recent developments of the Microchip Imaging Cytometer from the following aspects: clinical applications, microfluidic chip integration, imaging optics, and image acquisition. Following, we provide an outlook of the field and remark on promising technologies that may enable significant progress in the near future.The Microchip Imaging Cytometer (MIC) is a class of integrated point-of-care detection systems based on the combination of optical microscopy and flow cytometry. MIC devices have the attributes of portability, cost-effectiveness, and adaptability while providing quantitative measurements to meet the needs of laboratory testing in a variety of healthcare settings. Based on the use of microfluidic chips, MIC requires less sample and can complete sample preparation automatically. Therefore, they can provide quantitative testing results simply using a finger prick specimen. The decreased reagent consumption and reduced form factor also help improve the accessibility and affordability of healthcare services in remote and resource-limited settings. In this article, we review recent developments of the Microchip Imaging Cytometer from the following aspects: clinical applications, microfluidic chip integration, imaging optics, and image acquisition. Following, we provide an outlook of the field and remark on promising technologies that may enable significant progress in the near future.
Imaging polarimetry is one of the most widely used analytical technologies for object detection and analysis. To date, most metasurface-based polarimetry techniques are severely limited by narrow operating bandwidths and inevitable crosstalk, leading to detrimental effects on imaging quality and measurement accuracy. Here, we propose a crosstalk-free broadband achromatic full Stokes imaging polarimeter consisting of polarization-sensitive dielectric metalenses, implemented by the principle of polarization-dependent phase optimization. Compared with the single-polarization optimization method, the average crosstalk has been reduced over three times under incident light with arbitrary polarization ranging from 9 μm to 12 μm, which guarantees the measurement of the polarization state more precisely. The experimental results indicate that the designed polarization-sensitive metalenses can effectively eliminate the chromatic aberration with polarization selectivity and negligible crosstalk. The measured average relative errors are 7.08%, 8.62%, 7.15%, and 7.59% at 9.3, 9.6, 10.3, and 10.6 μm, respectively. Simultaneously, the broadband full polarization imaging capability of the device is also verified. This work is expected to have potential applications in wavefront detection, remote sensing, light-field imaging, and so forth.Imaging polarimetry is one of the most widely used analytical technologies for object detection and analysis. To date, most metasurface-based polarimetry techniques are severely limited by narrow operating bandwidths and inevitable crosstalk, leading to detrimental effects on imaging quality and measurement accuracy. Here, we propose a crosstalk-free broadband achromatic full Stokes imaging polarimeter consisting of polarization-sensitive dielectric metalenses, implemented by the principle of polarization-dependent phase optimization. Compared with the single-polarization optimization method, the average crosstalk has been reduced over three times under incident light with arbitrary polarization ranging from 9 μm to 12 μm, which guarantees the measurement of the polarization state more precisely. The experimental results indicate that the designed polarization-sensitive metalenses can effectively eliminate the chromatic aberration with polarization selectivity and negligible crosstalk. The measured average relative errors are 7.08%, 8.62%, 7.15%, and 7.59% at 9.3, 9.6, 10.3, and 10.6 μm, respectively. Simultaneously, the broadband full polarization imaging capability of the device is also verified. This work is expected to have potential applications in wavefront detection, remote sensing, light-field imaging, and so forth.