View fulltext
View fulltext
ObjectivesThe rapid integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into maritime technology has driven unprecedented advancements in unmanned surface vehicles (USVs), positioning them as a crucial force in future maritime operations
The purpose of this work is to optimize the communication architecture for existing remotely-controlled ships to meet the challenges of network connectivity in diverse environments (e.g., ports, deep-sea, and polar regions), aimin
Systematic testing, verification and reliability evaluation of autonomous navigation capability are important prerequisites for the industrial application of intelligent ships. To clarify the requirements of different test objects
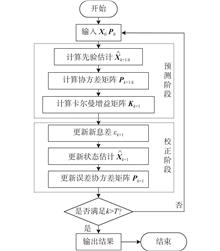
ObjectivesTo construct an accurate MMG (mathematical model group) model for a water-jet propulsion unmanned surface vehicle, the traditional extended Kalman filter algorithm and improved extended Kalman filter algorithm are combin
ObjectivesAiming at the requirements of the real-time and accurate prediction of ship maneuvering motion, this paper investigates the prediction of ship maneuvering motion in regular waves using gray-box modelling to improve the a
ObjectiveAiming to address the problem of model inaccuracy caused by ship dynamic changes during actual navigation, this study proposes an adaptive online modeling method for ship maneuvering motion based on an error monitoring me
ObjectivesTo address the issue of multicollinearity and parameter drift in the identification of hydrodynamic coefficients in ship separated-type models, this paper proposes a method for modeling simplified three-degree-of-freedom
ObjectiveAiming at the low prediction precision and poor adaptability of ship models based on the data-driven modeling strategy, an enhanced bi-directional long short-term memory (Bi-LSTM) model is proposed for the high-precision
ObjectiveIt is difficult to achieve comprehensive parameter identification in multiple dimensions and degrees of freedom using traditional parameter identification methods. In order to obtain the real-time complex parameters and a
ObjectiveDue to mixed-frequency multi-source disturbances, unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) encounter challenges in accurately capturing state information and ensuring path-tracking precision. To address this issue, a composite an
ObjectiveThe traditional model predictive control method employs a repeated online optimization approach, resulting in a high computational burden for underactuated ship path-following predictive controller. To address this issue,
ObjectivesA dynamic event-triggered collaborative path-following control method for multiple unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) is proposed, considering the constraints of network bandwidth resources, model uncertainties, and extern
ObjectivesA data-driven trajectory tracking control scheme is proposed for unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) with uncertain parameters. MethodsFirst, the USV kinematics subsystem is processed by the backstepping, and we can obtain
ObjectiveAiming at the problems of unknown ship model parameters and external disturbance and servo constraints, this paper proposes a method for the data-driven online identification of ship parameters and iterative analytical ca
ObjectiveThis paper presents a novel approach to the precise control of variable mass unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) during payload deployment tasks, addressing the control challenges caused by unpredictable variations in both m
ObjectiveThis study investigates how to effectively address path-dependent constraints during the path-following of unmanned surface vessels in complex waterways while ensuring navigation safety and stability. MethodFirst, perform
ObjectiveIn order to solve the track-keeping problem of a fishing vessel under rough sea conditions, a separated track-keeping controller is proposed.MethodsThe nonlinear feedback method is used to improve the closed-loop gain sha
ObjectivesIntelligent ships at sea are influenced by environmental interference, and the influence of the uncertainty of model parameters leads to the problem of low ship motion control accuracy, so it is necessary to improve the
Objective In the process of marine resource development, some thrusters of over-actuated ships are prone to failures during operation, resulting in a decrease in propulsion power. This paper aims to propose a fault-tolerant contro
ObjectiveThe heave and pitch motions of a catamaran under severe sea states vary drastically, and the amplitudes of the motions are too large, which seriously affects seaworthiness. To address this problem, this paper proposes a f
ObjectiveAn adaptive neural control (ANC) scheme with specified performance is proposed for the tracking control of marine autonomous surface ships (MASS) subject to uncertain model parameters and unknown external environmental di
ObjectiveThis study aims to solve the problem of path-following control under environmental disturbances and model uncertainties, especially the effects of external wind and wave environments. MethodBased on a model predictive con
ObjectivesThis paper seeks to provide a solution for the formation control issue that arises when autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) are subjected to interference from obstacles and complex ocean currents. Methods To tackle the
ObjectiveTo address the covert communication requirements of autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs), this study proposes a near-surface communication mode equipped with a foldable antenna.MethodsUtilizing strip theory to predict th
ObjectiveIn order to improve the robustness of autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) controllers to environment modeling errors, this paper proposes a reinforcement learning control strategy that introduces contextual information an
ObjectivesTo improve the ability of autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) formations to perform tasks in complex obstacle scenarios, a distributed three-dimensional affine formation shape maneuver control method is proposed for mult
ObjectiveIn order to improve the economy and safety of ship navigation path in actual sea environment, this paper proposes a ship global path planning method with an improved Deep Q-Network (DQN) algorithm.MethodFirst, a prioritiz
ObjectiveTo address the challenges of path planning for unmanned surface vehicles in complex waters, this paper proposes an improved ant colony optimization(ACO)algorithm based on uneven distributed pheromone and multi-objective o
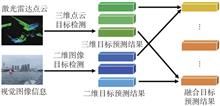
ObjectiveMaintaining consistent tracking of surface ships using unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) is particularly challenging due to the target's high maneuverability and complex motion trajectories. Additionally, environmental int
Objectives To make local path planning algorithms more consistent with the maneuvering characteristics of ships, thereby generating safer and more reliable reference paths, this paper proposes a three-dimensional potential field m
ObjectivesTo enhance the safety and efficiency of maritime traffic, this paper proposes an autonomous collision avoidance decision-making method for unmanned ships based on an enhanced Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG) alg
ObjectivesConsidering that existing research on autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) obstacle avoidance mainly focuses on low-speed obstacle avoidance for small and medium-sized AUVs and overly simplifies the diverse constraints wi