View fulltext
View fulltext
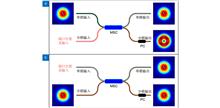
Far-field super-resolution microscopic imaging technology based on fluorescent labels opened a gate to the microscopic world, which has become an important tool in the research of modern medicine and life science. However, the development of far-field unlabeled super-resolution microscopy is relatively slow. Here, an integrated differential microscopic imaging method using optical fiber devices is proposed in this article. The generation of hollow spots in the differential imaging system is realized by a special fiber mode selection coupler (MSC). The problem of strict alignment between hollow and solid spots is naturally solved in this method. A highly integrated label-free microscopic imaging system was established. In experiments, gold particles with a diameter of 150 nm and unlabeled polymer lines with a minimum spacing of about 50 nm were imaged to test the imaging system. The resolution of the imaging system shows great improvement compared to conventional scanning confocal microscopy.
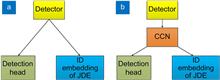
Due to the difficulties of complex backgrounds and large-scale differences between objects during the process of ship multi-object tracking in sea-surface scenarios, an improved CSTrack algorithm for ship multi-object tracking is proposed in this paper. Firstly, as violent decoupling is used in the CSTrack algorithm to decompose neck features and cause object feature loss, an improved cross-correlation decoupling network that combines the Res2net module (RES_CCN) is proposed, and thus more fine-grained features can be obtained. Secondly, to improve the tracking performance of multi-class ships, the decoupled design of the detection head network is used to predict the class, confidence, and position of objects, respectively. Finally, the MOT2016 dataset is used for the ablation experiment to verify the effectiveness of the proposed module. When tested on the Singapore maritime dataset, the multiple object tracking accuracy of the proposed algorithm is improved by 8.4% and the identification F1 score is increased by 3.1%, which are better than those of the ByteTrack and other algorithms. The proposed algorithm has the advantages of high tracking accuracy and low error detection rate and is suitable for ship multi-object tracking in sea-surface scenarios.
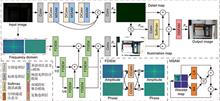
Aiming at the problems of poor low-light image quality, noise, and blurred texture, a low-light enhancement network (DF-DFANet) based on dual-frequency domain feature aggregation is proposed. Firstly, a spectral illumination estimation module (FDIEM) is constructed to realize cross-domain feature extraction, which can adjust the frequency domain feature map to suppress noise signals through conjugate symmetric constraints and improve the multi-scale fusion efficiency by layer-by-layer fusion to expand the range of the feature map. Secondly, the multispectral dual attention module (MSAM) is designed to focus on the local frequency characteristics of the image, and pay attention to the detailed information of the image through the wavelet domain space and channel attention mechanism. Finally, the dual-domain feature aggregation module (DDFAM) is proposed to fuse the feature information of the Fourier domain and the wavelet domain, and use the activation function to calculate the adaptive adjustment weight to achieve pixel-level image enhancement and combine the Fourier domain global information to improve the fusion effect. The experimental results show that the PSNR of the proposed network on the LOL dataset reaches 24.3714 and the SSIM reaches 0.8937. Compared with the comparison network, the proposed network enhancement effect is more natural.
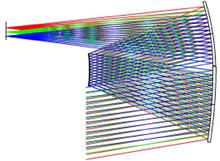
In order to meet the requirements of miniaturization, compact structure and high resolution of the space optical systems in the fields of Earth remote sensing observation and spaceborne Lidar detection, this paper designs a compact off-axis triple inverse system based on Zernike free-form surface, which simultaneously meets the requirements of long focal length, small distortion and wide working band. The system adopts an off-axis triple inverse optical system with the asymmetric and nearly circular layout, and the third mirror of the system adopts the free-form surface design. By setting appropriate optimization objectives and methods in Zemax software, the design of the optical system is optimized. Finally, the effective focal length of the system is 800 mm, the F-number is 4, the field of view is 12°×6°, and the distortion is less than 1%. The working band covers the visible and near/middle infrared bands, and the ground element resolutions of 1.5 m (visible light) and 2.5 m (near infrared) can be achieved at the orbit height of 400 km, and the ground width is 80 km×40 km. The analysis and verification of system aberration, dot plot, MTF and other performance indexes are carried out. The results show that the design scheme brings the high resolution and improves the information acquisition ability.
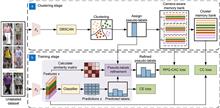
Unsupervised person re-identification has attracted more and more attention due to its extensive practical application prospects. Most clustering-based contrastive learning methods treat each cluster as a pseudo-identity class, overlooking intra-class variances caused by differences in camera styles. While some methods have introduced camera-aware contrastive learning by partitioning a single cluster into multiple sub-clusters based on camera views, they are susceptible to misguidance from noisy pseudo-labels. To address this issue, we first refine pseudo-labels by leveraging the similarity between instances in the feature space, using a weighted combination of the nearest neighboring predicted labels and the original clustering results. Subsequently, it dynamically associates instances with possible category centers based on refined pseudo-labels while eliminating potential false negative samples. This method enhances the selection mechanism for positive and negative samples in camera-aware contrastive learning, effectively mitigating the influence of noisy pseudo-labels on the contrastive learning task. On Market-1501, MSMT17 and Personx datasets, mAP/Rank-1 reached 85.2%/94.4%, 44.3%/74.1% and 88.7%/95.9%.
There are several major challenges in the detection and identification of contraband in millimetre-wave synthetic aperture radar (SAR) security imaging: the complexities of small target sizes, partially occluded targets and overlap between multiple targets, which are not conducive to the accurate identification of contraband. To address these problems, a contraband detection method based on dual branch multiscale fusion network (DBMFnet) is proposed. The overall architecture of the DBMFnet follows the encoder-decoder framework. In the encoder stage, a dual-branch parallel feature extraction network (DBPFEN) is proposed to enhance the feature extraction. In the decoder stage, a multi-scale fusion module (MSFM) is proposed to enhance the detection ability of the targets. The experimental results show that the proposed method outperforms the existing semantic segmentation methods in the mean intersection over union (mIoU) and reduces the incidence of missed and error detection of targets.
A method for preparing microlens arrays based on projection lithography was proposed, and microlens arrays of various calibers and different surface roughness were successfully prepared by the method. The method employs a 0.2× projection objective lens to reduce the manufacturing cost of masks and realize the preparation of microlens arrays with different calibers. We achieve superior surface figure accuracy while reducing the complexity of mask preparation by employing a projection-based mask-shift filtering technique. Four kinds of microlens arrays with different calibers, 50 μm, 100 μm, 300 μm and 500 μm, were prepared. The machining accuracy of the surface morphology reaches the sub-micron level and the surface roughness reaches the nanometer level. The experimental results show that this method has great potential in the fabrication of microlens arrays, and can achieve lower line width and higher surface profile accuracy than traditional methods.